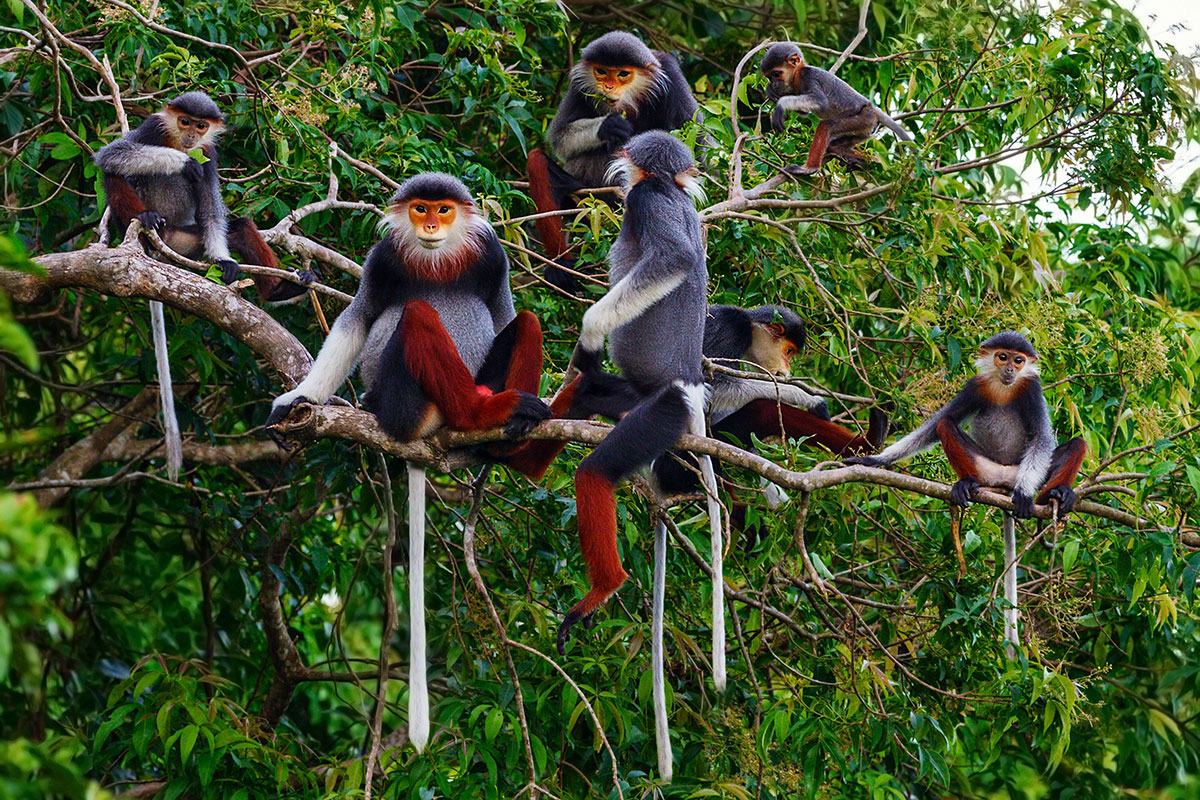
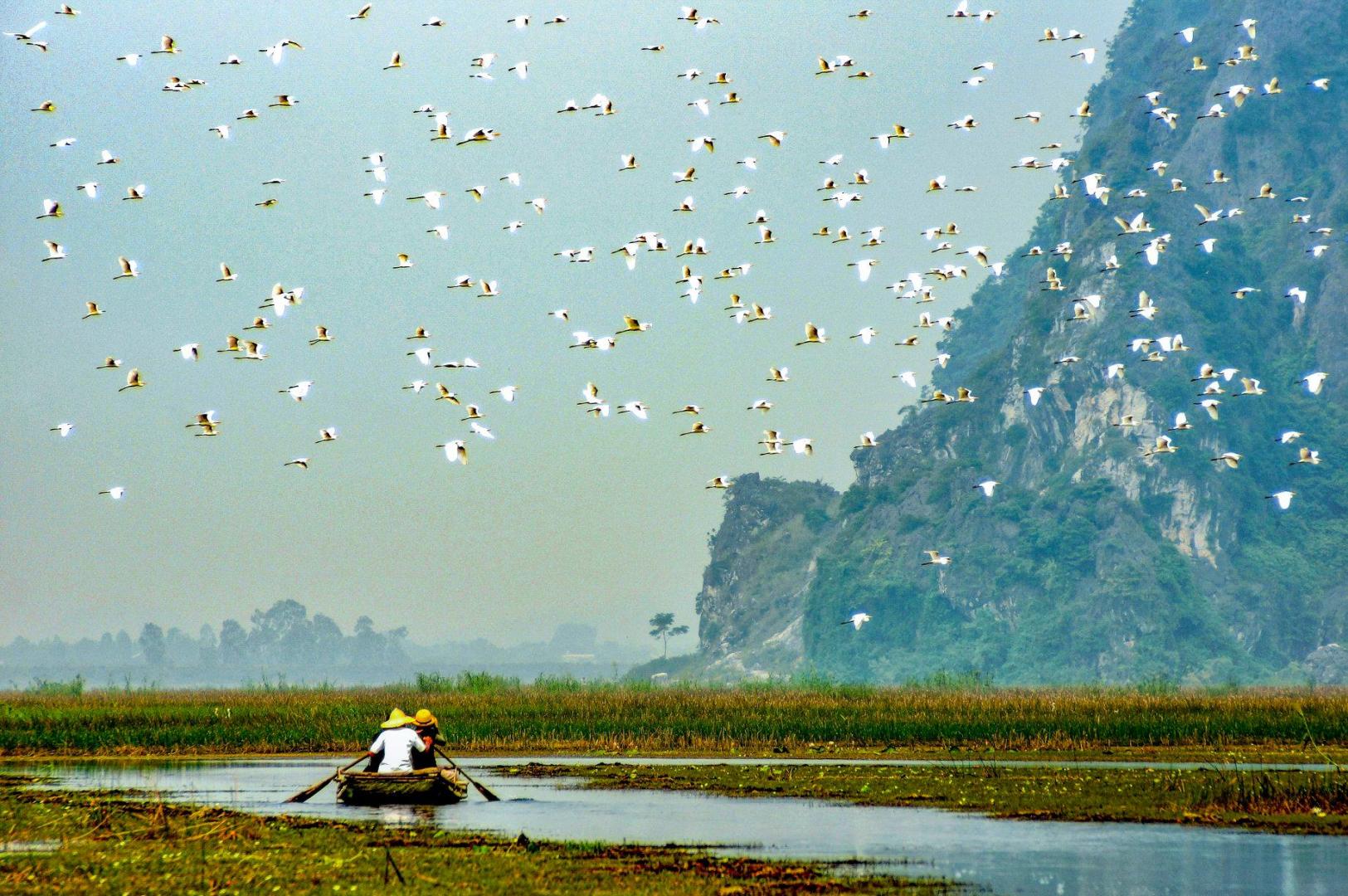
As one of the countries with high biodiversity in the world, Vietnam has many guidelines and policies to protect, preserve and promote biodiversity.
Despite many achievements in perfecting the legal framework and law enforcement on wildlife management and protection, Vietnam still faces many challenges due to illegal trafficking, storage, and transportation of wild animals. Promote activities to protect wildlife is an important task for both competent agencies and society as a whole.

Intensifying the fight against biodiversity crimes
The National Strategy on Biodiversity until 2030, which has been approved by the Prime Minister, set out specific tasks to realise national conservation goals and contribute to successful implementation of global targets adopted at the post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework.
The strategy aims to improve the population status of at least 10 endangered, precious and rare species that are prioritised for protection. To this end, the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment has submitted to the Prime Minister for approval a conservation programme for endangered, precious and rare species prioritised for protection.

Significant efforts have been made by relevant authorities in the fight against wildlife trafficking.
The Education for Nature-Vietnam (ENV) recorded 2,760 incidents with 8,661 wildlife-related violations in the first nine months of 2023. Authorities have seized more than 2,000 living wild animals and arrested those involved in 110 cases.
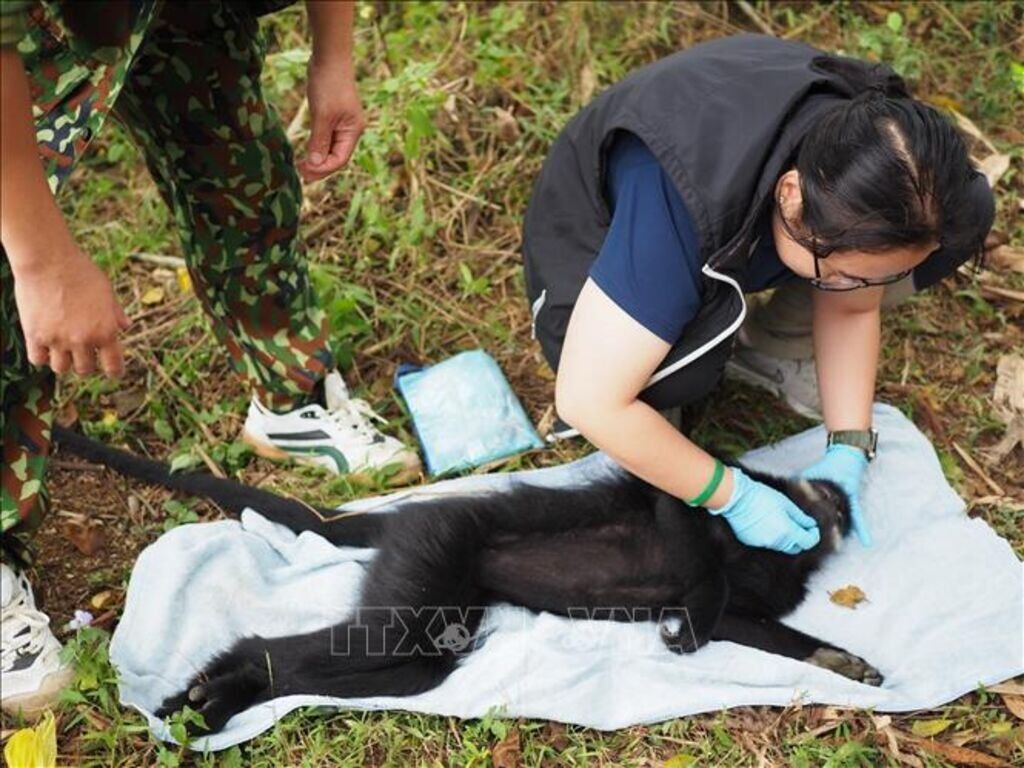
Of the 145 cases of wildlife-related violations brought to trial during the reviewed period, prison sentences were applied to violators in 63 of the cases. Those who illegally advertised, kept and traded wild animals were fined a total 13.4 billion VND (547,300 USD), the ENV said.
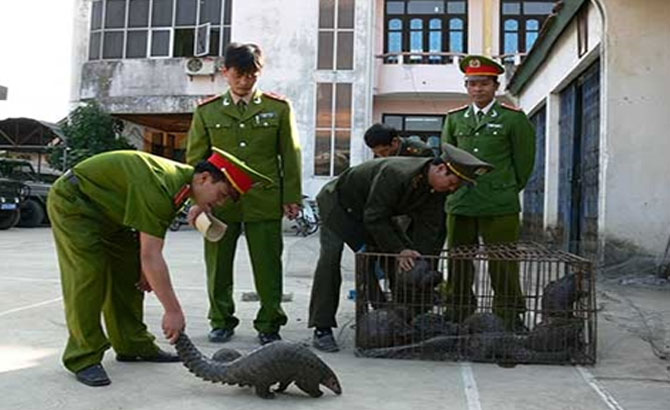

Along with commercial farming activities that are not strictly controlled, one of the problems that causes public concern is the illegal import of exotic animals and plants. According to the ENV, nearly 300 violations have been reported over the past two years with more than 9,700 individuals of exotic wild animals being trafficked or kept in captivity.

Vice Chairman of the National Assembly (NA)’s Committee for Judicial Affairs Nguyen Manh Cuong said that great efforts have been exerted by the NA and the Government in fine-tuning the legal system and strengthening the handling of violations. However, wildlife-related crimes are still common with many cases involving the transport of wildlife in large quantities. Some foreigners take advantage of Vietnam as a transit point for the wildlife trafficking trade.
It is necessary for competent agencies to strengthen law enforcement, thereby, raising awareness of people and civil servants on the protection of wildlife, including not using wildlife products, he added.

According to Nguyen Phuong Dung, ENV Deputy Director, actions such as using wildlife drugs, wearing ivory jewelry, and decorating the house with wildlife specimens, keeping monkeys as pets, storing or advertising wild birds for sale on the Internet are serious threats to the country’s biodiversity.

Biodiversity conservation efforts
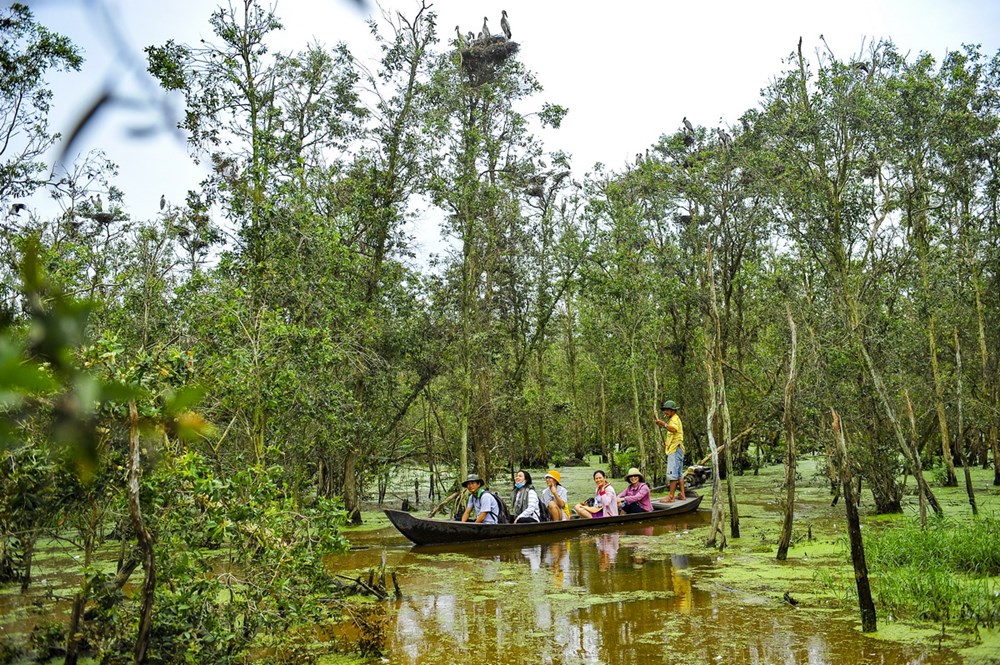
According to a report from the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (MONRE), Vietnam has implemented many biodiversity conservation solutions to expand the nature reserves network. The country has so far established 178 conservation zones, including 34 national parks, 59 nature reserves, 23 species-habitat conservation areas, and 62 landscape protection areas.

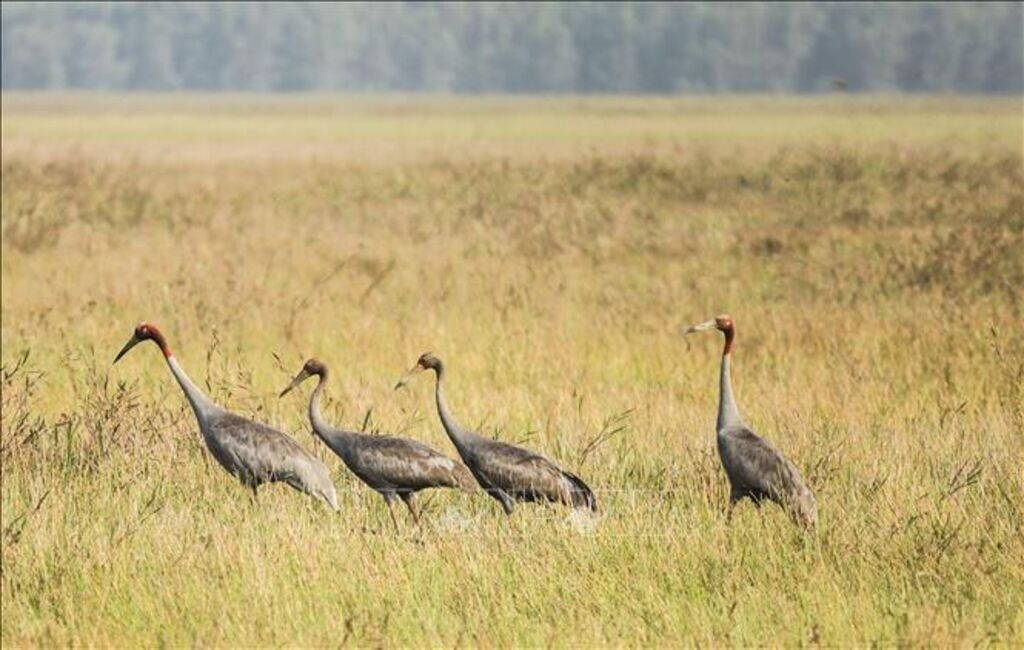
Tram Chim National Park in the southern province of Dong Thap was named the 2,000th Ramsar site in the world and the fourth in Vietnam in 2012. It is a the habitat and feeding ground for 232 bird species, including 32 rare ones of which 16 are endangered.
The park is a favourite habitat for red-crowned cranes, an endangered bird species listed in the Red Book of Vietnam and International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List of threatened species. The park witnessed 1,052 of red-crowned cranes arrive in 1988. Only three ones reported left by 2021. The red-crowned crane has not returned to the park over the past two years.
Climate change and the socioeconomic development in Dong Thap province have affected the biodiversity of Tram Chim National Park. To preserve and sustainably exploit resource values, the province has devised a range of plans and solutions to prevent biodiversity loss in the locality. It has launched a project on conservation and development of red-crowned cranes at Tram Chim National Park for 2022-2023 with total capital of nearly 185 billion VND (7.5 million USD).

Vietnam targets to end bile farming across the country by the end of 2026. The first phase of the Bear Rescue Centre has been inaugurated at Bach Ma National Park in central province of Thua Thien-Hue’s Phu Loc district by the Animals Asia Foundation in partnership with the Forest Protection Department under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
The centre includes a veterinary hospital and various zones for bear food preparation, awareness education, and waste treatment, among others along with other infrastructure. It helps solve the problems relating to lack of facilities to care for wild animals that are voluntarily handed over by local residents or seized by competent agencies.

One of the solutions to promote species conservation in the coming time is to combine in-situ and ex-situ conservation work for endangered, precious and rare animal species that are prioritised for protection as well as gradually apply advanced international conservation methods in line with Vietnam’s actual conditions. In-situ and ex-situ conservation measures are priority actions to be implemented in parallel with measures to reduce threats to species./.
