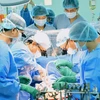
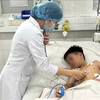
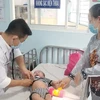
Hanoi (VNS/VNA) - The expansion of remote medical examination and treatment has helped both patients and healthcare workers, especially in mountainous and remote areas, access advanced techniques.
The Ministry of Health has carried out a project on remote medical examination and treatment for the 2020-2025 period which aims to strengthen the professional capacity of grassroots-level healthcare establishments as well as spread the professional knowledge of doctors from central-level hospitals to people and health workers across the country.
According to Assoc., Dr. Luong Ngoc Khue, Director of the Medical Examination and Treatment Department, technology used in examination and treatment through the telemedicine programme is a big change, with the goal of developing the healthcare sector in a modern direction and approaching international standards.
Technology makes communication easier between medical facilities across the country with a huge amount of information exchanged directly at any time.
Advances in technology give doctors more time in the race to save lives.
“For example, echocardiography is a difficult technique in medicine. Thanks to the technology and telemedicine programme, doctors in Hanoi can monitor the echocardiography for patients in mountainous and remote areas,” the director said.
“Doctors at central-level hospitals can coordinate with doctors in many other provinces and cities to consult and treat severe cases at grassroots healthcare facilities so patients do not need transferring to other hospitals,” he said.
Currently, people can book medical examinations and treatment appointments in many hospitals by phone, or through internet applications without having to queue and register.
Thanks to the technology application in medical examination and treatment, patients not only have access to advanced medical examination and treatment services but also save time, costs and reduce risks during treatment.
According to Khue, during the two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical examination and treatment system has continuously increased the application of information technology solutions and digital transformation, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment in the country.
"More than 3,000 cases have been consulted for medical examination and treatment remotely. Over 1,100 consultation sessions were conducted with 32,000 online locations, 155 patients with critical condition were saved,” Khue said.
“However, nearly 38% of healthcare establishments have not yet implemented automatic queuing to ensure fairness for patients. And cash payment for hospital fees still accounts for nearly 30%," he said.
The Ministry of Health will continue to review and complete policies on information technology and digital transformation in medical examination and treatment and issue the circular on e-prescribing; telemedicine, and fees for telemedicine and consultation.
Therefore, hospitals need to strictly implement documents of the Government and Ministry of Health on information technology and digital transformation as well as improve the capability of informatics staff.
According to Nguyen Truong Nam, vice director of the Informatics Department (Health Ministry), healthcare is one of the eight priorities of national digital transformation specified in the Government's Decision No. 749/QD-TTg.
Under the decree, all public healthcare facilities must establish telemedicine sections, build and gradually form a healthcare and disease prevention system based on digital technologies, and comprehensively apply digital technology at medical examination and treatment facilities so as to contribute to administrative reform, reducing overloading in hospitals, and improve the quality of medical examination and treatment.
The public hospitals will use electronic medical records and hospital fee payments, forming smart hospitals and smart health management platforms based on digital technology, integrating information and data in order to form a national database on health.
Medical facilities deploy the initiative "Each Citizen Has a Personal Doctor" with the goal that each person has a digital record of personal health that they are consulted and cared for by doctors, contributing to forming a complete digital healthcare system from primary health care, prevention to treatment.
Additionally, a legal corridor should be set up to facilitate remote medical examination and treatment and e-prescriptions for patients to ensure that people can contact doctors quickly and efficiently to reduce costs of examination, treatment and patient transfer as well./.
The Ministry of Health has carried out a project on remote medical examination and treatment for the 2020-2025 period which aims to strengthen the professional capacity of grassroots-level healthcare establishments as well as spread the professional knowledge of doctors from central-level hospitals to people and health workers across the country.
According to Assoc., Dr. Luong Ngoc Khue, Director of the Medical Examination and Treatment Department, technology used in examination and treatment through the telemedicine programme is a big change, with the goal of developing the healthcare sector in a modern direction and approaching international standards.
Technology makes communication easier between medical facilities across the country with a huge amount of information exchanged directly at any time.
Advances in technology give doctors more time in the race to save lives.
“For example, echocardiography is a difficult technique in medicine. Thanks to the technology and telemedicine programme, doctors in Hanoi can monitor the echocardiography for patients in mountainous and remote areas,” the director said.
“Doctors at central-level hospitals can coordinate with doctors in many other provinces and cities to consult and treat severe cases at grassroots healthcare facilities so patients do not need transferring to other hospitals,” he said.
Currently, people can book medical examinations and treatment appointments in many hospitals by phone, or through internet applications without having to queue and register.
Thanks to the technology application in medical examination and treatment, patients not only have access to advanced medical examination and treatment services but also save time, costs and reduce risks during treatment.
According to Khue, during the two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical examination and treatment system has continuously increased the application of information technology solutions and digital transformation, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment in the country.
"More than 3,000 cases have been consulted for medical examination and treatment remotely. Over 1,100 consultation sessions were conducted with 32,000 online locations, 155 patients with critical condition were saved,” Khue said.
“However, nearly 38% of healthcare establishments have not yet implemented automatic queuing to ensure fairness for patients. And cash payment for hospital fees still accounts for nearly 30%," he said.
The Ministry of Health will continue to review and complete policies on information technology and digital transformation in medical examination and treatment and issue the circular on e-prescribing; telemedicine, and fees for telemedicine and consultation.
Therefore, hospitals need to strictly implement documents of the Government and Ministry of Health on information technology and digital transformation as well as improve the capability of informatics staff.
According to Nguyen Truong Nam, vice director of the Informatics Department (Health Ministry), healthcare is one of the eight priorities of national digital transformation specified in the Government's Decision No. 749/QD-TTg.
Under the decree, all public healthcare facilities must establish telemedicine sections, build and gradually form a healthcare and disease prevention system based on digital technologies, and comprehensively apply digital technology at medical examination and treatment facilities so as to contribute to administrative reform, reducing overloading in hospitals, and improve the quality of medical examination and treatment.
The public hospitals will use electronic medical records and hospital fee payments, forming smart hospitals and smart health management platforms based on digital technology, integrating information and data in order to form a national database on health.
Medical facilities deploy the initiative "Each Citizen Has a Personal Doctor" with the goal that each person has a digital record of personal health that they are consulted and cared for by doctors, contributing to forming a complete digital healthcare system from primary health care, prevention to treatment.
Additionally, a legal corridor should be set up to facilitate remote medical examination and treatment and e-prescriptions for patients to ensure that people can contact doctors quickly and efficiently to reduce costs of examination, treatment and patient transfer as well./.
VNA