All three major carriers, including VinaPhone, MobiFone, and Viettel, have started their 5G journey by announcing the trial of the service in big cities like Hanoi, HCM City at the end of 2020. (Photo courtesy of Viettel)
All three major carriers, including VinaPhone, MobiFone, and Viettel, have started their 5G journey by announcing the trial of the service in big cities like Hanoi, HCM City at the end of 2020. (Photo courtesy of Viettel) The Dau tu (Investment) Newspaper organised a talk titled “Getting 5G Ready for Vietnam’s Digital Transformation” on April 4.
All three major carriers, including VinaPhone, MobiFone, and Viettel, have started their 5G journey by announcing the trial of the service in big cities like Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City at the end of 2020 and then consecutively expanded to other cities.
The 5G network was commercially tested by three operators, Viettel, VNPT and MobiFone, in 16 provinces and cities by the end of last year.
Nguyen Hoa Cuong, vice president of the Central Institute of Economic Management (CIEM), said that about 70 countries around the world had commercialised 5G.
Besides being a technological innovation on its own, 5G was the enabler for many other technologies, he added.
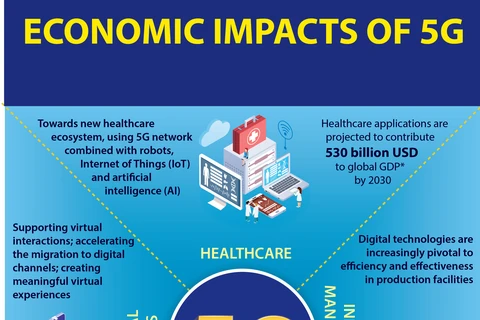
Vietnam is aspiring to develop a digital government, digital economy and digital society, and 5G is expected to play a fundamental role by enhancing broadband connection, improving rural coverage, creating conditions to narrow the digital divide, developing Industry 4.0 and increasing the contribution of the digital media sector to Vietnam's GDP.
An important component of Vietnam's socio-economic development strategy is the development of the digital economy, which is expected to contribute 7 percent of GDP by 2025 and 7.5 percent by 2030.
The Ministry of Information and Communications has set a goal to officially license 5G commercialisation this year and soon cover high-tech industrial parks.
The information and communication industry is determined to bring Vietnam along as a leading country in 5G.
The Ministry of Information and Communications is currently in the final preparation steps to officially license 5G network operators this year.
However, for the successful commercialisation of 5G, problems still need to be solved.
To commercialise 5G faster, Vietnam needs sufficient bandwidth, ripe 5G technology, diversified 5G services, and numerous cheap terminal equipment.
Investment in 5G infrastructure is also a matter of concern. In the context of rising investment costs and declining telecommunications revenue, 5G investment is not simple.
According to experts, tightening spending and investing in the common use of infrastructure and networks are key solutions for network operators to implement in Vietnam successfully.
This is just one of many solutions to the problem. Reducing investment costs also lies in choosing technology, using foreign equipment or self-manufacturing, and optimising markets and human resources costs.
These will be issues that network operators need to calculate more carefully in the near future./.
VNA