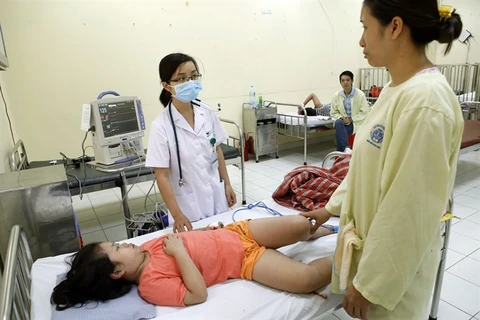
HCM City (VNA) - Many hospitals in HCM City use software to monitor the prescription of antibiotics to ensure they are not abused causing bacteria to mutate to become antibiotic-resistant, a major global health problem, including in Vietnam.
The Hospital for Tropical Diseases in District 5, for instance, has since May 2016 used a software to approve and dispense antibiotics prescribed by its doctors. All computers in the hospital are connected to the host system.
If the department chief disapproves the prescription, the clinic staff do not issue the antibiotics.
In the past doctors used to write their prescriptions on paper, and this would be sent to department heads, the pharmacy, and its board of directors for approval.
The hospital realised the system was too unwieldy and sometimes meant patients could not be provided drugs in time.
It also caused difficulties in maintaining data, and the software has helped resolve these problems, according to the hospital.
The Gia Dinh People’s Hospital in Binh Thanh district was also one of the first in the city to use IT to manage the use of drugs, including antibiotics.
According to the hospital, antibiotic abuse has caused many bacteria to become rapidly resistant to drugs, and without preventive methods patients’ health would have been severely affected.
It began to use IT to manage antibiotic use in 2015.
Following the introduction of the programme, the rate of compliance with the antibiotics use regime improved dramatically. For instance, at the neurological surgery department it went up from 11 percent in 2015 to 65 percent in 2016.
The management board has to approve any prescription of antibiotics doctors make before they are dispensed.
The hospital has designated the antibiotics that can be used and the list is in its electronic system.
Its doctors have also evaluated antibiotic resistance and the results of antibiotic use on patients and updated medical protocols.
They have reduced the course of antibiotic treatment from 11 days to eight now.
At Cho Ray Hospital, the use of an electronic surveillance system in 2014 has helped significantly reduce the use of antibiotics.
In 2015 only 64 percent of the antibiotics used in 2014 was prescribed, and the cost of antibiotics for patients came down by 46 billion VND (2 million USD).
The city Department of Health encourages all hospitals to use IT to help their doctors use antibiotics properly and their chiefs monitor prescriptions.
Electronic surveillance could warn doctors prescribing multiple antibiotics that they are not needed or could have side-effects if used together, it said.
Both doctors and patients should be educated in the proper use of antibiotics to avoid resistance, it said.
The city has more than 6,000 private medical stores, and this is a major challenge to health authorities since people have the habit of self-prescribing antibiotics when ill, it said.
The pharmacies would be instructed to use IT to generate data on antibiotics so that it can monitor them, it said.
According to the World Health Organisation, antibiotic resistance can affect people of any age.
It also occurs naturally, but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process.
A growing number of infections – such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhoea, and salmonellosis – are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them have become less effective.-VNA
The Hospital for Tropical Diseases in District 5, for instance, has since May 2016 used a software to approve and dispense antibiotics prescribed by its doctors. All computers in the hospital are connected to the host system.
If the department chief disapproves the prescription, the clinic staff do not issue the antibiotics.
In the past doctors used to write their prescriptions on paper, and this would be sent to department heads, the pharmacy, and its board of directors for approval.
The hospital realised the system was too unwieldy and sometimes meant patients could not be provided drugs in time.
It also caused difficulties in maintaining data, and the software has helped resolve these problems, according to the hospital.
The Gia Dinh People’s Hospital in Binh Thanh district was also one of the first in the city to use IT to manage the use of drugs, including antibiotics.
According to the hospital, antibiotic abuse has caused many bacteria to become rapidly resistant to drugs, and without preventive methods patients’ health would have been severely affected.
It began to use IT to manage antibiotic use in 2015.
Following the introduction of the programme, the rate of compliance with the antibiotics use regime improved dramatically. For instance, at the neurological surgery department it went up from 11 percent in 2015 to 65 percent in 2016.
The management board has to approve any prescription of antibiotics doctors make before they are dispensed.
The hospital has designated the antibiotics that can be used and the list is in its electronic system.
Its doctors have also evaluated antibiotic resistance and the results of antibiotic use on patients and updated medical protocols.
They have reduced the course of antibiotic treatment from 11 days to eight now.
At Cho Ray Hospital, the use of an electronic surveillance system in 2014 has helped significantly reduce the use of antibiotics.
In 2015 only 64 percent of the antibiotics used in 2014 was prescribed, and the cost of antibiotics for patients came down by 46 billion VND (2 million USD).
The city Department of Health encourages all hospitals to use IT to help their doctors use antibiotics properly and their chiefs monitor prescriptions.
Electronic surveillance could warn doctors prescribing multiple antibiotics that they are not needed or could have side-effects if used together, it said.
Both doctors and patients should be educated in the proper use of antibiotics to avoid resistance, it said.
The city has more than 6,000 private medical stores, and this is a major challenge to health authorities since people have the habit of self-prescribing antibiotics when ill, it said.
The pharmacies would be instructed to use IT to generate data on antibiotics so that it can monitor them, it said.
According to the World Health Organisation, antibiotic resistance can affect people of any age.
It also occurs naturally, but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process.
A growing number of infections – such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhoea, and salmonellosis – are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them have become less effective.-VNA
VNA