Hanoi (VNA) - The Ministry of Health has issued a warning that the current season, when students gather for the new school year, is the time when the number of hand-foot-mouth disease cases among children is on the rise.
The possibility of an outbreak is high in this weather when summer changes to autumn, accompanied by rainfall, unless authorities and health offices take prompt preventive measures, the Department of Preventive Medicine under the ministry warned.
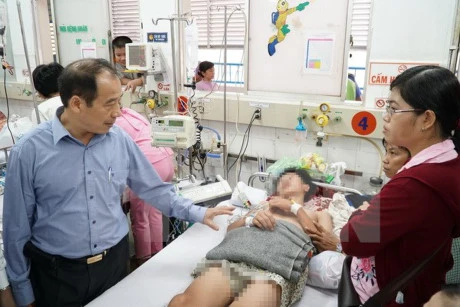
In Hanoi over the last week, 12 children were hospitalised for treatment of hand-foot-mouth disease, while there were 121 cases reported in Ho Chi Minh City.
Associate Professor Tran Dac Phu, Director of the Preventive Medicine Department, said hand-foot-mouth disease is an acute viral infection transmitted by the digestive tract. The disease is common in infants and likely to cause severe epidemics.
It is very contagious if hygiene measures are not followed. In Vietnam, the number of cases tends to increase between March and May and from September to December.
The department’s statistics showed that since the beginning of this year, there were 51,218 cases of hand-foot-mouth cases nationwide, of which 23,272 patients were hospitalised.
The number of hospitalisation cases increased by 3.4 percent against the same period last year.
Interestingly, the number of cases tended to increase in recent weeks, and was predicted to continue to rise in the coming weeks when students returned to school, as this was also the time for a change of season.
According to health experts, the disease is most contagious in the first week after a patient is infected and may last for several weeks due to the virus focal in the waste. Signs of the disease are fever, sore throat, oral mucosal lesions and skin mainly in the form of scalds commonly found on the palms, soles of the feet, knees and buttocks.
Most cases are mild. However, in some cases, the disease can be severe and dangerous complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis and acute pulmonary edema that could lead to death should be detected early to ensure timely treatment
The hand-foot-mouth disease mainly occurs in children under the age of 10, and particularly in those under five. The smaller the child is, the more serious the symptoms are.
All those who have not suffered from the disease are at risk of infection when they come in contact with infected instruments or surfaces, but not everyone who is infected with the virus shows signs of the disease, Phu said.
Pregnant women should especially avoid close contact with an infected person since the virus can be transmitted to the baby either before birth or during childbirth. It is notable that a person can be infected multiple times because every time he or she is infected, the body produces antibodies to a specific virus. Therefore, even if a person has been infected once, the disease can return if infected with another virus belonging to the Enterovirus group.-VNA
The possibility of an outbreak is high in this weather when summer changes to autumn, accompanied by rainfall, unless authorities and health offices take prompt preventive measures, the Department of Preventive Medicine under the ministry warned.
In Hanoi over the last week, 12 children were hospitalised for treatment of hand-foot-mouth disease, while there were 121 cases reported in Ho Chi Minh City.
Associate Professor Tran Dac Phu, Director of the Preventive Medicine Department, said hand-foot-mouth disease is an acute viral infection transmitted by the digestive tract. The disease is common in infants and likely to cause severe epidemics.
It is very contagious if hygiene measures are not followed. In Vietnam, the number of cases tends to increase between March and May and from September to December.
The department’s statistics showed that since the beginning of this year, there were 51,218 cases of hand-foot-mouth cases nationwide, of which 23,272 patients were hospitalised.
The number of hospitalisation cases increased by 3.4 percent against the same period last year.
Interestingly, the number of cases tended to increase in recent weeks, and was predicted to continue to rise in the coming weeks when students returned to school, as this was also the time for a change of season.
According to health experts, the disease is most contagious in the first week after a patient is infected and may last for several weeks due to the virus focal in the waste. Signs of the disease are fever, sore throat, oral mucosal lesions and skin mainly in the form of scalds commonly found on the palms, soles of the feet, knees and buttocks.
Most cases are mild. However, in some cases, the disease can be severe and dangerous complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis and acute pulmonary edema that could lead to death should be detected early to ensure timely treatment
The hand-foot-mouth disease mainly occurs in children under the age of 10, and particularly in those under five. The smaller the child is, the more serious the symptoms are.
All those who have not suffered from the disease are at risk of infection when they come in contact with infected instruments or surfaces, but not everyone who is infected with the virus shows signs of the disease, Phu said.
Pregnant women should especially avoid close contact with an infected person since the virus can be transmitted to the baby either before birth or during childbirth. It is notable that a person can be infected multiple times because every time he or she is infected, the body produces antibodies to a specific virus. Therefore, even if a person has been infected once, the disease can return if infected with another virus belonging to the Enterovirus group.-VNA
VNA