Hanoi (VNS/VNA) - Health experts have called for coordinated disease prevention efforts and integrated solutions to achieve zero dengue-related deaths in Vietnam, during an online talk show held on June 14.
The event was jointly organised by Suc khoe & Doi song (Health & Life) newspaper under the Ministry of Health, in collaboration with Takeda Vietnam, in celebration of ASEAN Dengue Day (June 15).
With the theme “Towards Zero Dengue Deaths: Collective Disease Prevention with Integrated Solutions”, the event aimed to foster multi-sectoral dialogue and raise public awareness, particularly in light of the World Health Organization (WHO) identifying dengue as one of the top ten global health threats.
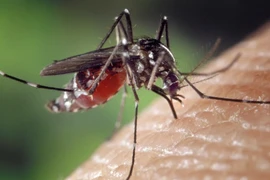
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly half of the world’s population, around 3.9 billion people, is at risk of dengue virus infection. Each year, approximately 500,000 cases require hospitalisation, and up to 25,000 people die from the disease globally.
In response, WHO has set a global target of achieving zero dengue deaths by 2030, as outlined in the Global Strategy for Dengue Prevention and Control 2021–2030. This strategic roadmap highlights key actions including early outbreak detection and response, sustainable vector control, community engagement, and efficient vaccine deployment.
During the discussion, speakers analysed the current state of dengue in Vietnam, highlighted emerging challenges, and proposed integrated strategies tailored to the country’s evolving epidemiological landscape.
Experts noted that dengue fever continues to impose a significant burden on public health in Vietnam. The number of cases fluctuates in the hundreds of thousands annually, and the disease is becoming increasingly unpredictable, occurring year-round, across wide geographical areas, and carrying risks of severe complications or death if not detected and treated promptly.
According to the Ministry of Health, as of mid-2025, Vietnam had reported 22,974 dengue cases and five deaths, with fatalities recorded in Ho Chi Minh City, Binh Duong, Binh Thuan, Khanh Hoa, and Ninh Thuan provinces. These figures underscore the continued threat posed by dengue, particularly amid overlapping outbreaks such as hand-foot-and-mouth disease and COVID-19, which are resurging in several localities.
From a regulatory standpoint, Dr. Vo Hai Son, Deputy Director of the Vietnam Administration of Disease Prevention under the Ministry of Health, emphasised: “In the fight against dengue fever, no single force can tackle the issue alone. A synchronised and collaborative approach is essential.”
“Government agencies play the role of coordinators and policymakers; the community is the frontline in actively detecting and treating the disease early, and tackling small outbreaks through vector control measures at the household level, particularly in high-risk areas. Enterprises contribute by offering medical solutions, communication support, and training, while the media serves as a crucial bridge to deliver accurate and timely information to every citizen.”
“Only when all these stakeholders act proactively, in unity and with persistence, can the epidemic control strategy be truly effective and sustainable. These combined efforts align with the goal set by the WHO: zero dengue deaths by 2030,” Son said.
To reduce fatalities and effectively control outbreaks, experts highlighted the need for a comprehensive strategy. This includes vector control, epidemiological surveillance, early warning systems, behaviour change communication, and strengthening the capacity of the healthcare system. Among these, vaccination, a new solution validated by the World Health Organization, is considered an integral component, supporting proactive prevention and reducing the risk of severe illness.
Associate Professor Dr. Pham Quang Thai, Deputy Head of the Infectious Diseases Control Department at the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, said: “In addition to the traditional ‘detection–response’ approach, Vietnam needs to shift towards a ‘forecast–prevention’ model to keep pace with changes in epidemic cycles and geographic spread. Dengue is no longer seasonal and can occur year-round. Therefore, investing in active surveillance systems, data analysis, and early warning mechanisms is essential for sustainable outbreak control. This calls for a holistic prevention strategy, including mosquito control, reduced community transmission, vector management, and boosting immunity through vaccination.”
Beyond the challenges of extreme weather and rapid urbanisation, public underestimation of dengue fever remains a critical concern.
Associate Professor Dr. Do Duy Cuong, Director of the Bach Mai Institute of Tropical Medicine, stressed: “Many people still underestimate dengue, thinking it is only dangerous when accompanied by high fever or visible bleeding. As a result, they delay seeking medical attention. Early detection and timely treatment save lives. As both a doctor and a survivor of dengue fever, I fully understand the burden and complications this disease can cause. Today, vaccination is a key preventive measure, offering a new and effective approach to tackling the complex nature of dengue.”
Benjamin Ping, General Manager of Takeda Vietnam, said:" We believe that effective control requires a multi-sectoral approach - bringing together by the government, the healthcare sector, businesses, and communities - under a comprehensive strategy. This includes strengthening healthcare capacity, raising public awareness about the dangers of dengue through collaborative community programs with relevant ministries and agencies, and ensuring a sustainable vaccine supply for the people of Vietnam."
The talk show also underscored the important role of community communication, not only as a means of raising awareness but also as a powerful tool for behaviour change. When people understand the disease correctly and act early, it significantly reduces the number of severe cases, late hospitalisations, and deaths./.
Dengue fever becomes more unpredictable: experts
Dengue fever is evolving to become more unpredictable and spread on a larger scale, heaping pressure on the healthcare system, experts have warned, noting that rapid urbanisation and climate change are further complicating challenges to disease prevention and control.