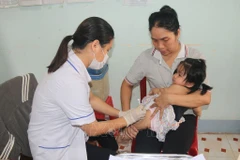
Hanoi (VNA) – The grassroots-level health carenetwork has been expanded nationwide, basically meeting public demand forhealth care, said Health Minister Nguyen Thi Kim Tien.
Speaking at a working session of the National Assembly’sCommittee for Social Affairs in Hanoi on August 7, Minister Tien highlightedachievements in vaccination, maternal and child health care, and the preventionof non-communicable diseases at the ward/commune level.
She cited the inpatient satisfaction index towards medicalcheck-up and treatment of 79.6 percent between September 2016 and December2017, along with the 2016 Provincial Governance and Public AdministrationPerformance Index (PAPI) Report announced in April 2017 which showed that thequality of hospitals, especially those at the district level, has been improvedsignificantly and people have satisfied more with medical services.
Deputy Minister of Planning and Investment Nguyen Van Hieusaid that thanks to investments sourced from Government bonds, hospitals andmedical centres at the district level have been built or upgraded, with thenumber of sickbeds per 10,000 people increasing from 17.9 in 2005 to 25.7 in2017, surpassing the target assigned by the legislature.
Participants at the working session also pointed outlimitations in the grassroots health care network regarding public confidencein the quality of medical establishments at the district and commune levels,primary health care, investments in grassroots-level health care, and humanresources.
They shared the views that more investments should bechanneled into grassroots health care, and underlined the need to mobilise theparticipation of different economic sectors and finalise the legal framework topromote the engagement of the entire political sector in the network.
It is necessary to allocate mid-term capital in the health sector,especially in remote, disadvantaged and ethnic minority-inhabited areas, theysaid, proposing the Health Ministry implement policies to attract and maintainpersonnel for grassroots health care establishment. -VNA