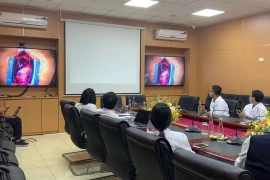
Hanoi (VNS/VNA) - In April 2020, during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, Hanoi Medical University Hospital launched its first trial telehealth sessions, connecting doctors in the capital with patients in Lao Cai, Ha Tinh and Thanh Hoa provinces.
Since then, the telehealth model has expanded rapidly, now connecting hundreds of health stations across the country with thousands of patients — both Vietnamese and foreign nationals.
Supported by international partners, the Ministry of Health continues to promote the model as a strategic solution to improving healthcare accessibility.
Assisted by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), since 2020 the ministry has deployed the 'Doctor for Everyone' telehealth software in eight provinces: Ha Giang, Bac Kan, Lang Son, Thua Thien-Hue, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Dak Lak and Ca Mau.
The ministry is currently working with the Korea Foundation for International Healthcare (KOFIH) and UNDP to implement the project 'Telehealth to Improve Access to Healthcare Services for Disadvantaged Groups in Vietnam'.
The project targets 10 remote and mountainous provinces still facing barriers in accessing healthcare.
Over the past six months, 150 communal health stations in provinces including Ha Giang, Bac Kan, Lang Son, Lao Cai, Lai Chau, Yen Bai, Tay Ninh, Hau Giang, Ben Tre and Ca Mau have been equipped with information technology systems. In addition, 117 key provincial healthcare workers have received training, with thousands more expected to follow.
Deputy Minister of Health Tran Van Thuan said telehealth reflects the modernisation of healthcare in Vietnam, helping expand equitable access to medical services, especially in underprivileged areas.
“Telehealth is a practical, humanitarian and meaningful model of international cooperation,” he said.
“It contributes to realising the goal of leaving no one behind in community healthcare.”
He said telehealth is a strategic breakthrough for the healthcare sector as Vietnam builds a modern, efficient and equitable national health system.
Associate Professor Nguyen Lan Hieu, director of Hanoi Medical University Hospital, said Vietnam is well-positioned to advance telehealth, given the Government’s commitment to digital transformation and a high internet penetration rate, with approximately 73.2% of the population — nearly 75 million people — online.
“With early adoption of telehealth at Hanoi Medical University Hospital, we believe combining traditional medical care with digital technology will enhance treatment efficiency and further the hospital’s reputation,” he said at a recent Vietnam–RoK telehealth workshop.
“Digital transformation cannot be applied uniformly. It must be customised to suit each institution or locality. This calls for close coordination not only among domestic institutions but also with international partners,” he said.
The hospital has been a pioneer in adopting technology in healthcare management, including electronic medical records, telemedicine, telepathology, tele-intensive care units and tele-education. It has conducted over 3,500 teleconsultations and 1,200 health check-ups since 2020, with participation from about 165 doctors.
Hieu noted that telehealth has significantly reduced travel time and patient waiting times while improving access to specialised services. Patients can join consultations via private video calls or dedicated mobile apps.
However, he acknowledged two major challenges: the cost and limited efficiency.
“Few patients register for telehealth because they have not yet seen its full benefits. Telehealth must demonstrate greater help than AI tools like ChatGPT or common messaging platforms such as Viber or Zalo,” he said.
To enhance adoption, he suggested integrating patient-tracking devices for at-home consultations.
His hospital aims to trial the devices with over 1,000 patients to evaluate satisfaction.
“In the long term, Vietnam should aim to produce its own medical devices to better serve domestic needs,” Hieu said.
Health experts agree that building a robust database of online health records is essential for the growth of telehealth.
Director General of the Department of Medical Service Administration Ha Anh Duc said the department is working to complete around 40 million electronic medical records this year and to establish health profiles for all citizens starting from birth. These profiles will be updated with regular health check-up results.
Dr Nguyen Van Linh from the Department of Health of Yen Bai province, one of the first localities to adopt telehealth under the KOFIH partnership, proposed creating a smart healthcare ecosystem with three core pillars: electronic medical records, AI-assisted diagnosis and telehealth services.
“These elements should be integrated into the VNeID app for convenient access for citizens,” he said.
Linh added that in many countries, telehealth is most effective during patients’ follow-up visits. Once patients have a digital medical history, telehealth becomes far more efficient.
With the national deadline for applying electronic medical records set for September, Yen Bai plans to begin widespread implementation in July, he said./.

See more

Vietnam ranks 4th in health self-care readiness
Self-care is an essential component of primary healthcare, with WHO defining it as the ability of individuals, families, and communities to promote and maintain health, prevent disease, and cope with illness with or without the support of healthcare professionals.
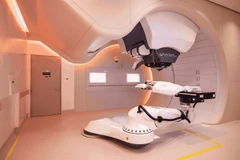
Proton therapy, an alternative method for cancer patients
In recent years, Vietnam's Ministry of Health has held numerous meetings with relevant units to assess the progress in developing proton therapy centres in the country. The project for establishing proton therapy centres is set to commence preparations in 2025 and aims for completion between 2026 and 2030.

First hospital in Mekong Delta earns US AACI accreditation
Nam Can Tho University Hospital on December 15 hosted a ceremony to announce its accreditation by the American Accreditation Commission International (AACI), a US-based body, becoming the first facility in the Mekong Delta and among a select few in Vietnam to earn the distinction.
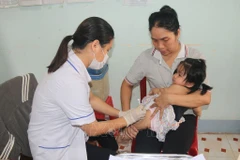
Vietnam proactively takes polio prevention measures amid outbreak in Laos
The meeting took place following an assessment by the World Health Organisation (WHO) warning that Vietnam is facing a very high risk of polio import and re-emergence. The risk arises after neighbouring Laos officially declared a polio outbreak on October 7, following the detection of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 1 (cVDPV1).

WHO welcomes Vietnam’s strong stance on banned e-cigarettes, heated tobacco products
WHO Representative in Vietnam Dr Angela Pratt said, “WHO is delighted with the decision to include e-cigarettes and HTPs in the list of banned enterprises under the Investment Law, without exceptions. This is crucial for upholding the National Assembly’s ban on these products – Resolution 173.”

Nearly 100 international scientists attend molecular diagnostics conference in Vietnam
The conference features almost 80 presentations across plenary sessions, parallel sessions and poster sessions, focusing on leading research trends such as point-of-care diagnostics; predictive biomarkers used to anticipate individual responses to therapy; and the development of new tools and platforms for rapid molecular-level detection and diagnosis.

French NGO ADM Vietnam marks 33 years of medical aid, language bridge
The association was established with three core missions: medical assistance, social support, and promotion of medical French - sending volunteer doctors to Vietnam, donating equipment, and helping medical students master French to secure clinical internships in France.
AI and precision medicine: Emerging prospects for Vietnam-Canada cooperation
Canada has strong experience in compiling and analysing genomic data, while Vietnam has a large population with diverse genetic structures. This complementarity can help Vietnam narrow its technological gap and enhance its capacity to treat rare diseases — an area many countries are prioritising for development.

Vietnam on path to become a healthy nation
Resolution 72 not only focuses on health care but is also closely interlinked with other sectors, helping to build a solid foundation for sustainable national development and create momentum for Vietnam to “take off” and further integrate into the world.

Legislators seek breakthrough mechanisms to mobilise social resources for elderly care
Existing social protection facilities currently meet only about 30% of demand.

Health sector targets free hospital fee for all
The total value of medical expenses not covered by the health insurance fund is estimated at around 24.8 trillion VND (942 million USD) per year. Health insurance contributions remain low, at 4.5% of the salary or reference base used for calculation.

Vietnam rolls out comprehensive programmes to curb HIV/AIDS
In 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) hailed Vietnam as a leading country in the Asia-Pacific region in HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) treatment.

Vietnam, Laos expand cooperation in military medicine
Over the past two decades, many Vietnamese experts have undertaken long-term missions at the Central Hospital 103 to provide training and technical assistance, contributing to the successful treatment of complex cases. The Central Military Hospital 108 has also trained 206 Lao doctors, six nurses and two engineers — a clear demonstration of substantive, long-standing cooperation.

Vietnam, Mexico boost medical cooperation
As both nations look to keep their long-standing partnership in good health, the health ministries of Vietnam and Mexico have been accelerating cooperation, especially in traditional medicines.

Major medical, pharmaceutical exhibitions kick off in HCM City
The 33rd Vietnam International Medical and Pharmaceutical Exhibition (Vietnam Medi-Pharm 2025) and the International Exhibition on Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices and Healthcare (Vietmedicare Expo 2025) kicked off at the Saigon Exhibition and Convention Centre on November 27.

Vietnam's healthcare system approaches international standards
The goal for the next decade is to bring Vietnam's quality standards closer to international benchmarks, promote independent certification, introduce quality-linked payment mechanisms, and expand digital transformation.
Organs from neurologically deceased donors save 29 lives within two weeks
Surgeons at the 108 Military Central Hospital successfully carried out a multi-organ transplant using organs from a brain-dead donor on November 22, marking two consecutive weeks in November during which the hospital has helped save 29 patients.

Vietnam prioritises protecting youth from new-generation tobacco products
“Our duty is to protect future generations through strong, decisive and evidence-based policies.”

Vietnamese surgeons honoured with prestigious Royal College Fellowship
The fact that the Vietnamese doctors have been awarded with FRCS certificate proves Vietnam’s surgical expertise has met international standards, contributing to improving the quality of treatment at home, expanding academic cooperation with world leading medical institutions and inspiring younger doctor to pursue higher standards.
Vietnam affirms global standing in organ transplantation
In mid-August, Viet Duc University Hospital announced that its doctors successfully performed Vietnam’s first-ever combined heart–lung transplant, marking a major step forward for the country’s medical field.