Hanoi (VNA) – Super Typhoon Ragasa continues to intensify as it approaches the East Sea, bringing powerful winds, towering waves, and warnings of flash floods and landslides in northern mountainous provinces of Vietnam.
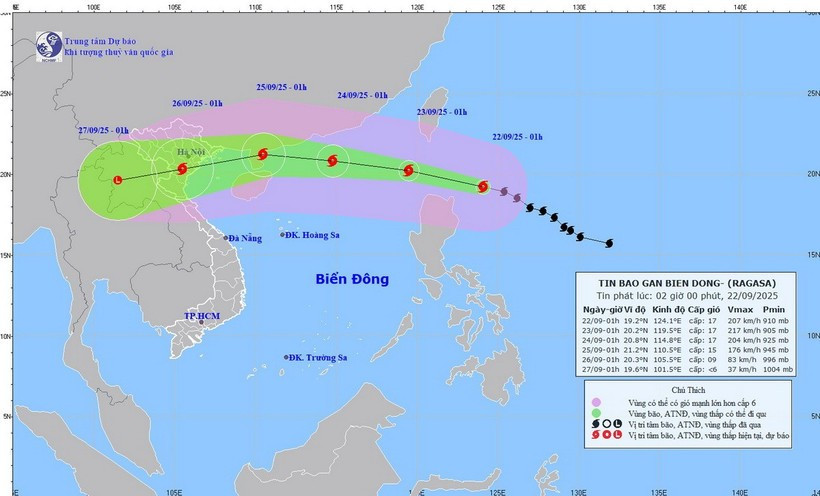
At 7 am on September 22, the storm’s eye was located at 19.3 degrees North latitude and 123.1 degrees East longitude, about 160 km northeast of Luzon Island in the Philippines. Ragasa packed maximum winds of 202–221 km per hour (equivalent to Level 17 on Vietnam’s wind scale), with gusts exceeding Level 17, and was moving west-northwest at around 20 km per hour, according to the National Centre for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting.
By 7 am on September 23, Ragasa is forecast to be in the northeastern region of the northern East Sea with sustained winds of Level 17, gusting above Level 17. It will likely continue to strengthen as it tracks west-northwest at 20 km per hour and enters East Sea. Disaster risk level has been set at Category 4, the second-highest warning.
By 7 am on September 24, the storm is expected to be about 370km east of China’s Leizhou Island, maintaining winds of Level 16–17 and gusts of over Level 17; moving west-northwest at 20 km per hour.

By 7 am about September 25, Ragasa is predicted to weaken to Level 13–14 with gusts exceeding Level 17. It will continue moving west at 15–20 km per hour before gradually abating.
Associate Professor Dr. Mai Van Khiem, Director of the forecasting centre, warned that the eastern part of the northern East Sea will see winds gradually strengthening from Level 8–9 to Level 10–14, and near the storm’s eye reaching Level 15–17 with gusts above Level 17. Waves could rise over 10 metres, making the sea extremely rough. All vessels in the affected waters face very high risks from squalls, strong winds, and high seas./.