Hanoi (VNA) – Vietnam currently ranks third in the world in cassava exports, but its cassava supply chain continues to face significant challenges, heard a meeting held in Hanoi on January 28.
The meeting, themed “Vietnam’s cassava supply chain: Current situation and challenges”, was jointly organised by the Vietnam Economic Science Association of Agriculture and Rural Development, the Vietnam Cassava Association, and Forest Trends.
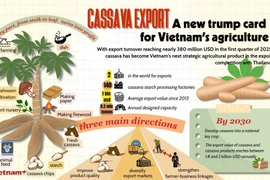
Speaking at the event, Nghiem Minh Tien, Chairman of the Vietnam Cassava Association, said cassava production, processing and trade play an important role in Vietnam’s agricultural trade and provide livelihoods for around 1.2 million farming households, mainly in midland, mountainous and disadvantaged areas. Alongside domestic consumption, cassava has posted strong export growth, with turnover in 2025 estimated at about 1.3 billion USD, making Vietnam the world’s third-largest cassava exporter.
Vietnam is both a major producer of raw cassava and a large processing and export hub in the region. Annual cassava supply exceeds 18 million tonnes of fresh roots, of which about 58% comes from domestic production and 42% from imports, mainly from Laos and Cambodia. Cassava cultivation area in Vietnam covers more than 500,000 hectares, producing roughly 10 million tonnes annually, while imports stand at about 8 million tonnes.
Participants noted that although export volumes have risen sharply, export value has grown more slowly. A key long-term solution is to increase added value through deeper processing. This includes gradually reducing exports of dried cassava chips and low-processed starch, while encouraging investment in high-tech products such as modified starch and products for the food, pharmaceutical, industrial and bioenergy sectors, thereby improving efficiency, sustainability and resilience to raw-material price fluctuations.
While several important policies have been issued, including the scheme on sustainable development of the cassava sector to 2030 with a vision to 2050, implementation remains limited due to the lack of detailed guidance, monitoring tools and sufficient incentives to ensure compliance with requirements on traceability, transparency and forest protection.
Meanwhile, despite a slight nationwide decline in cassava cultivation area in recent years, expansion has continued in some localities, raising concerns about impacts on forest resources. International markets are also tightening requirements on legality, traceability and deforestation-free products, notably the EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), posing growing challenges for Vietnam’s cassava exports.
Ha Cong Tuan, Chairman of the Vietnam Economic Science Association of Agriculture and Rural Development, pointed out that the biggest difficulty in ensuring traceability lies in the raw material stage, including supplies from both domestic farmers and foreign sources.
Nguyen Vinh Quang, representing Forest Trends, said the cassava sector needs to restructure its supply chain, strengthen control over production and land use, formalise informal activities and improve transparency across the chain to meet traceability requirements.
From the business perspective, Tien affirmed that cassava enterprises are committed to building a transparent and sustainable supply chain that meets forest protection, environmental and traceability standards. He also called on authorities to provide clearer guidance and appropriate support mechanisms to facilitate compliance with new requirements./.
Cassava exports — Vietnam’s new “trump card” for agriculture
To clearly define cassava’s role, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development has, for the first time, issued a Sustainable Development Plan for the cassava sector through 2030, with a vision extending to 2050.



























